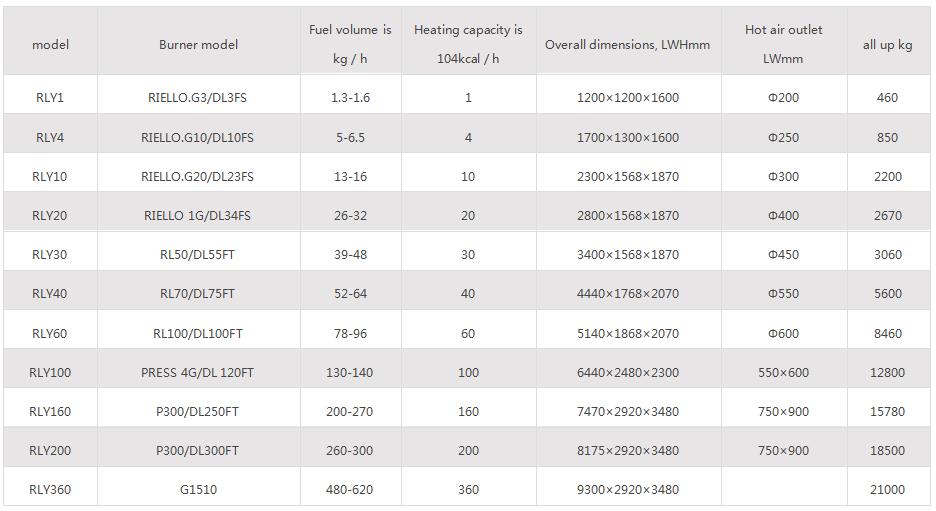
Fuel is burned through a burner to produce high-temperature gas. And with the help of a hot blast stove with enhanced heat exchange measures, the heat of the high-temperature gas is conducted to the heated air. After the heat is dissipated, the temperature of the high-temperature gas is reduced to 250 ℃ and discharged into the atmosphere. The air that needs to be heated is forcefully sent into the hot air stove through the optional blower. After absorbing heat, the temperature rises to the rated value and is sent out from the hot air outlet. When the hot air temperature reaches the upper limit of the rated temperature, the burner will automatically stop burning or switch to small flame combustion. When the hot air temperature drops to the lower limit of the rated temperature, the burner will reignite or switch to high flame combustion. The heating speed can be adjusted by adjusting the opening of the inlet valve.